What is Secure Remote Access?
Secure Remote Access implies the need for companies to protect their networks and data when their employees are accessing the internal resources outside of the office remotely or on a mobile device. With the increasing number of remote workers, hybrid working allowances, and the evolving threat landscape, organizations need to prioritize securing remote access to prevent […]
Author
Date
Category
All Categories
- AI-powered security
- Attacks & Threats
- Cybersecurity
- Hybrid Cloud
- Network
- Network Firewall
- Network Protection
- News
- Remote Workforce
- Security
- Zero Trust
Contents
Popular Posts
Product
Join the Newsletter

Secure Remote Access implies the need for companies to protect their networks and data when their employees are accessing the internal resources outside of the office remotely or on a mobile device. With the increasing number of remote workers, hybrid working allowances, and the evolving threat landscape, organizations need to prioritize securing remote access to prevent unauthorized access to their resources and sensitive data. In this article, we will explore the benefits of remote access, strategies to ensure its security, and what the organizations should look for when choosing a secure remote access solution.
Understanding Secure Remote Access
Secure remote access refers to the process of providing authorized individuals with controlled access to an organization’s network, systems, and confidential data from remote locations. It enables employees and third parties to connect to the internal network and access resources based on their roles and responsibilities. By implementing secure remote access strategies, organizations can protect their systems and applications while ensuring operational efficiency, and continued productivity.
Types of Secure Remote Access Strategies
There are several methods that organizations usually choose from when it comes to enabling secure remote access, each with their own pros and cons:
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): VPNs are widely used to establish secure connections over the internet by encrypting data and authenticating users. Traditional VPNs are clunky, and give access to company resources after a simple credentials check. If a hacker uses stolen VPN credentials to access the company network, they can then move laterally within the whole organization as VPNs don’t do network segmentation.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA):ZTNA is the modern solution to secure remote access, based on the principle of never trusting anyone or any device with remote access until they are completely and exhaustively verified. Additionally, the access is granted on the least privilege basis, meaning a user is allowed only to the portion of the network that he or she is authorized for, minimizing the blast radius in case of a breach.
- Desktop Sharing: Desktop sharing allows users to remotely access and control another device’s desktop or screen. It is a collaborative method that provides real-time access to data and files located on a different device.Desktop sharing comes with significant risks to a company’s cybersecurity posture due to its inherent weakness for depending on the users’ being diligent while they are accessing the remote desktops.
- Secure Shell (SSH) Remote Access: SSH is a network protocol that enables users to access a remote computer securely. It establishes a secure connection without the need for a password, providing authenticated access to a text-mode terminal on the remote computer.
- Network Access Control (NAC): NAC solutions manage and control access to an organization’s network through authentication, endpoint security measures, and network security policies. NAC helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures secure remote connections.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): SSO enables users to access multiple applications and resources using a single set of login credentials. It simplifies the authentication process and improves user experience while ensuring secure access.
- Context-Based Remote Access: Context-based access control applies different security controls based on various access contexts, such as user identity, device type, location, and time. It provides granular access controls tailored to specific access scenarios.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): PAM involves securing, managing, and monitoring privileged access and permissions for users, accounts, applications, systems, and processes. It ensures that privileged access is granted on a need-to-know basis and monitored for potential security breaches.
Why is Secure Remote Access Important?
Ability to provide secure remote access to an organization’s network and resources is critical to a company’s success. Key points for this are given below:
- Mitigating Risks: Remote access exposes organizations to potential security risks, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats. By implementing secure remote access measures, organizations can mitigate these risks and protect their sensitive data.
- Safeguarding Against Insider Threats: Remote access introduces the risk of insider threats, where employees with privileged access may misuse their privileges or fall victim to social engineering attacks. Secure remote access solutions help monitor and control these privileged sessions, reducing the risk of insider threats.
- Enhancing Productivity: Secure remote access enables employees to work from anywhere, improving productivity and work-life balance. Employees can access resources and collaborate with colleagues seamlessly, regardless of their physical location.
- Facilitating Third-Party Access: Secure remote access solutions allow organizations to grant temporary, role-based access to third parties, such as contractors or vendors. This ensures that third parties have limited access to specific resources required for their tasks, minimizing potential security risks.
- Ensuring Compliance: Many industries have regulatory compliance requirements regarding data privacy and security. Secure remote access solutions help organizations adhere to these regulations by implementing access controls, monitoring privileged sessions, and maintaining audit trails.
Best Practices for Secure Remote Access
To achieve truly secure remote access and minimize risks, organizations should rely on the following best practices.
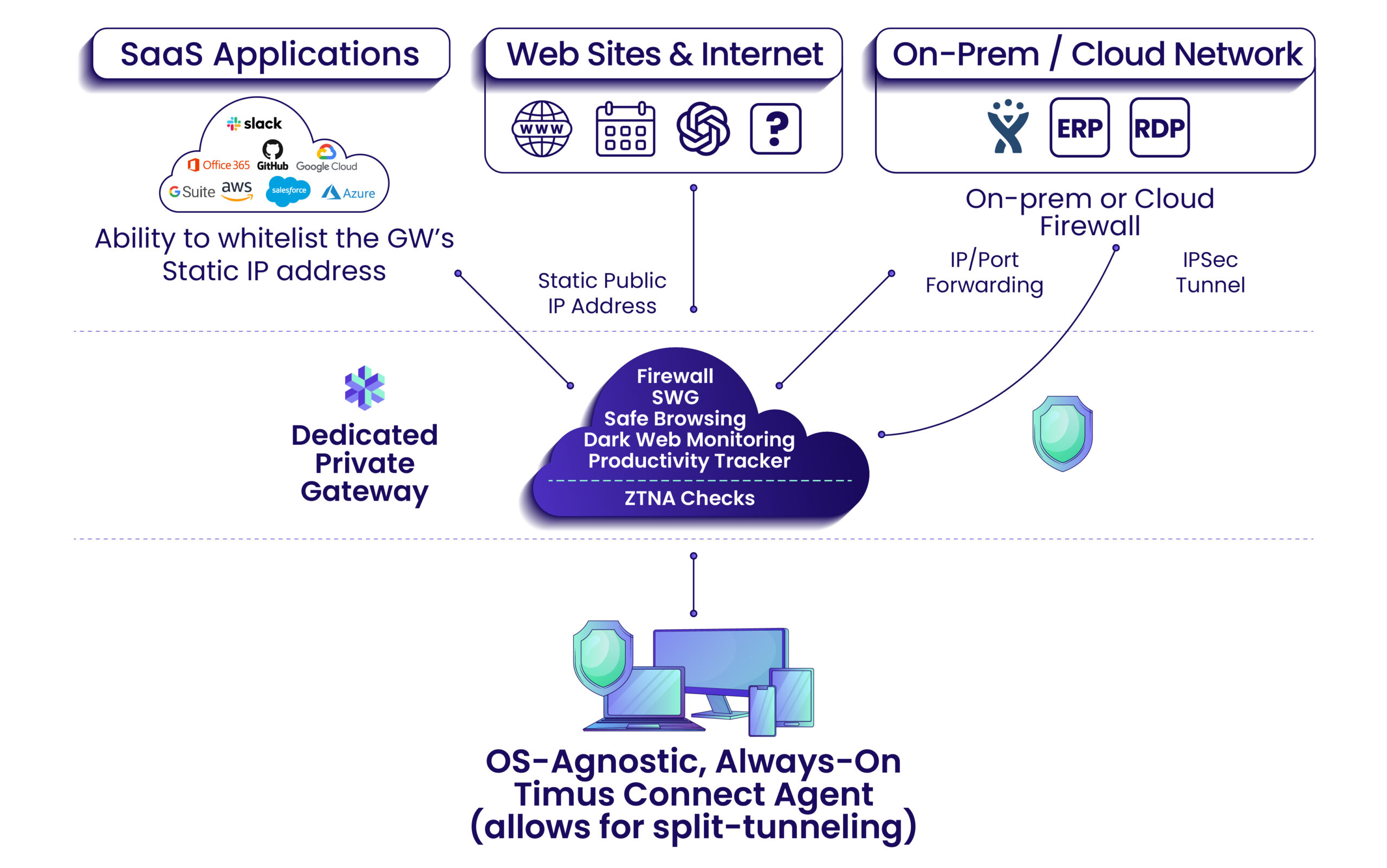
Use Zero-Trust Principles: With zero-trust, no one or no device is given access to the network until they are completely and exhaustively verified by a contextual policy engine. In addition to credentials, zero trust mechanisms check the context of the connection such as time and location, amongst others, before allowing access. Additionally, the access is granted on the least privilege basis, meaning a user is allowed only to the portion of the network that he or she is authorized for, minimizing the blast radius in case of a breach.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens. This mitigates the risk of unauthorized access even if one factor is compromised.
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): Grant users the minimum privileges necessary to perform their tasks. Restricting access rights to only what is required reduces the potential impact of compromised accounts and minimizes the risk of unauthorized actions.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keep all software, including remote access solutions, up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Regularly patching vulnerabilities helps prevent exploitation by malicious actors.
- Monitor and Audit Remote Sessions: Implement session monitoring and auditing to detect and respond to suspicious activities. Real-time monitoring and recording of remote sessions provide visibility into user behavior and help identify potential security incidents.
- Educate Users on Security Best Practices: Provide regular training to employees and users on remote access security best practices. This includes awareness of phishing attacks, password hygiene, and responsible use of remote access tools.
- Use Secure File Transfer Protocols: When transferring files remotely, utilize secure file transfer protocols, such as Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) or Secure Shell File Transfer Protocol (SSH File Transfer Protocol). These protocols encrypt data during transit, ensuring its confidentiality.
- Employ Endpoint Security Measures: Implement endpoint security solutions, such as antivirus software and firewalls, to protect devices connecting remotely to the network. Regularly update and patch these security tools to defend against the latest threats.
- Regularly Review Access Privileges: Conduct periodic reviews of user access privileges to ensure that they are aligned with roles and responsibilities. Remove or modify access rights for users who no longer require them, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Enforce Strong Password Policies: Implement strong password policies, requiring users to create complex passwords and regularly change them. Educate users on the importance of unique passwords and discourage password reuse across different services.
- Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest: Use encryption technologies, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or IPsec, to secure data during transmission. Additionally, consider implementing full-disk encryption to protect data stored on remote devices.
Choosing the Best Secure Remote Access Solution
Selecting the right secure remote access software is crucial for organizations seeking to establish robust remote access capabilities. Consider the following factors when evaluating different solutions:
- Security Features: Look for software that offers strong encryption, authentication mechanisms, and granular access controls. Ensure that the solution aligns with your organization’s security requirements and supports industry best practices.
- Compatibility and Integration: Evaluate whether the solution integrates seamlessly with your existing IT infrastructure and applications. Compatibility with different operating systems and devices is essential to provide a consistent user experience across platforms.
- User Experience: Consider the ease of use and intuitiveness of the software’s user interface. A user-friendly interface reduces the learning curve for employees and enhances productivity.
- Scalability and Performance: Assess the software’s ability to handle increasing user demands and scale with your organization’s growth. Performance is crucial to ensure a seamless remote access experience without significant latency or downtime.
- Vendor Reputation and Support: Research the vendor’s reputation in the market and their track record in providing reliable support and timely updates. Look for reviews and customer testimonials to gauge the vendor’s credibility.
- Compliance Capabilities: Ensure that the software complies with relevant industry regulations and standards. This includes features such as audit trails, session recording, and reporting capabilities for compliance audits.
Conclusion
Secure remote access is a critical component of modern organizations’ IT environments, enabling employees and third parties to connect to networks and resources from remote locations. By implementing secure remote access strategies and following best practices, organizations can mitigate security risks, enhance productivity, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Choosing the right secure remote access solution and vendor is essential to establishing a robust and secure remote access infrastructure. By prioritizing secure remote access, organizations can stay productive while staying secure.
Get Started with Timus
Zero Trust. Adaptive Cloud Firewall. Secure Remote Access. In one.
